この記事では、Arduinoで測定した温度をパソコンで表示する方法をソースコード付きで解説します。
気温を表示
Arduinoマイコンと温度センサ(LM35DZ)を用いて気温(温度)を計測し、その結果をシリアル通信でPCに転送してPythonでリアルタイム表示してみました。
回路構成(配線図)
Arduinoと電子部品の構成・配線は下記の通りです。
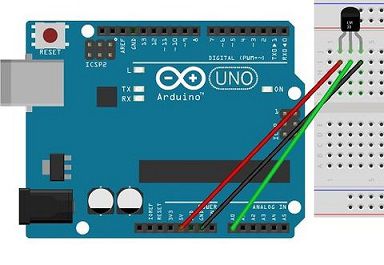
電子部品
・Arduino UNO (1個)
・温度センサ(LM35DZ)
・ジャンプワイヤー(数本)
ソースコード
サンプルプログラムのソースコードです。
Arduino側
float a_in; // アナログ入力値(0〜203)
float temp_c = 0; // 摂氏値( ℃ )
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600); // シリアル通信速度
}
void loop(){
// アナログピンから計測値を取得(0〜203)
a_in = analogRead(0);
// 入力値を摂氏に換算
temp_c = ((5 * a_in) / 1024) * 100;
// 改行しながら出力
Serial.println( temp_c );
// 1000ms待機
delay(1000);
}
Python(パソコン側)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import serial
import datetime
def queue(src, a):
dst = np.roll(src, -1)
dst[-1] = a
return dst
def main():
# 1次元配列の生成
temps = np.zeros(10)
i = 0
ser = serial.Serial("COM5") # Arduinoが接続されているコムポートを指定
while(i != 100):
todaydetail = datetime.datetime.today()
line = ser.readline() # 行終端まで読み込む
temp = line.rstrip() # 行終端コード削除
# キュー操作
temps = queue(temps, temp)
print('--------------------------------')
print(todaydetail.strftime("%Y/%m/%d %H:%M:%S"))
print("Temp:", temp)
print("Average:", np.average(temps))
print("Std:", np.std(temps))
i+=1
ser.close()
print("End")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
実行結果
サンプルプログラムの実行結果です。
コメント